Language :
Select your language
Application
Cr-Cu contacts are used in the vacuum arc-quenching chambers (VACs) of highly dependable, quick-acting vacuum circuit breakers capable of breaking large currents in high-voltage 6-35 kW electrical networks. Contacts are a key element in commutation switches (circuit breakers). Currently, the most common material used in contact pairs in VACs are Cr-Cu composites.
Contacts are subjected to the effects of short-circuit currents and fusing metals in various points of the surface due to the high density of the current in them; as a result, welding joints form in these zones. This problem was one reason that delayed the development of vacuum commutation technology for more than twenty years. The resistance of a VAC's contacts to welding is one of its key characteristics. The problem of welding was solved by developing special contact plates made from chromium-copper composites, which provided a high breaking capacity for circuit breakers in commutation networks, wear-resistance and resistance of contact pairs to welding together.
W-Cu contacts are used in VACs of vacuum contactors with a nominal voltage of 1.14 kW and higher in systems for remote control of electric drivers. The contacts are a long-lasting means of switching contactors in electric circuits on and off and ensure a low cut-off current in the system.
Grades, structure and chemical composition
| Grade,standard | Form and structure | Chemical composition, mass % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | Cu | O max | N max | S max | |||
| ERCr25Cu75-PM | Single-layer chromium-copper disks | 24-27 | Base | 0.07 | 0.005 | ND | |
| ERCr50Cu50-PM | Single-layer chromium-copper disks | Balance | 48-53 | 0.07 | 0.005 | ND | |
| ERCr35Cu65-PM | Single-layer chromium-copper disks | 33-37 | Base | 0.07 | 0.005 | ND | |
| ERCr30Cu70-PM | Two-layer disks: Cr-Cu and Cu | Contact layer | 27-33 | Balance | 0.05 | 0.005 | 0.007 |
| Copper layer | <1.0 | Base | 0.02 | 0.005 | 0.007 | ||
| ERCr50Cu50-PM | Contact layer | 48-53 | Balance | 0.05 | 0.005 | 0.007 | |
| Copper layer | <1.0 | Base | 0.02 | 0.005 | 0.007 | ||
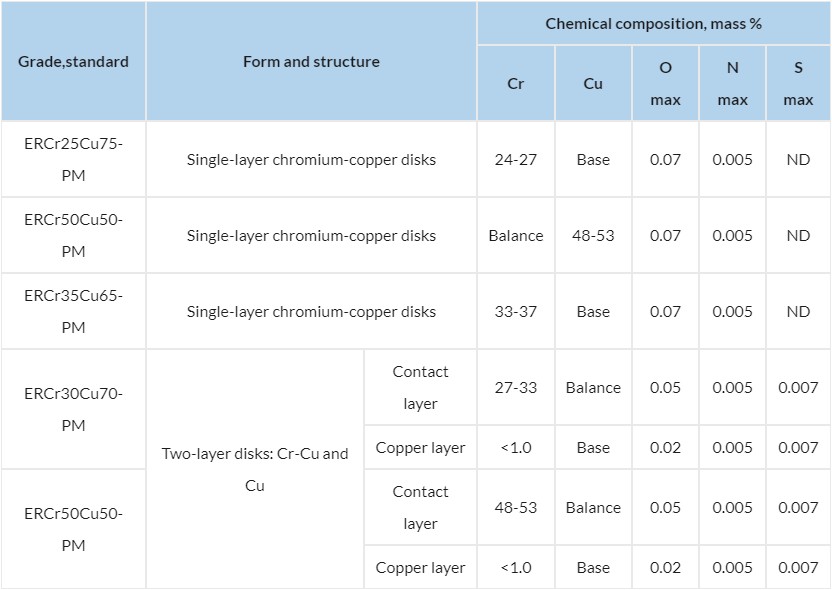
PM – Powder Metallurgy
Dimensions
| Grade | Nominal dimensions, mm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter | Thickness | |||
| Disc | Contact layer | Copper layer | ||
| ERCr25Cu75-PM single-layer discs | 90 | 8.0 to 20.0 | - | - |
| ERCr50Cu50-PM single-layer discs | 48, 56, 66, 70, 80 | 8.0 to 20.0 | - | - |
| ERCr35Cu65-PM single-layer discs | 42.0 to 90.0 | 7.0 to 13.0 | - | - |
| ERCr30Cu70-PM two-layer discs | 32 | 4.0 | 2±0.5 | 2±0.5 |
| 48, 56, 60, 66, 80 | 6.0 | 3±0.5 | 3±0.5 | |
| ERCr50Cu50-PM two-layer discs | 32 | 4.0 | 2±0.5 | 2±0.5 |
| 48, 56, 60, 66, 80 | 6.0 | 3±0.5 | 3±0.5 | |
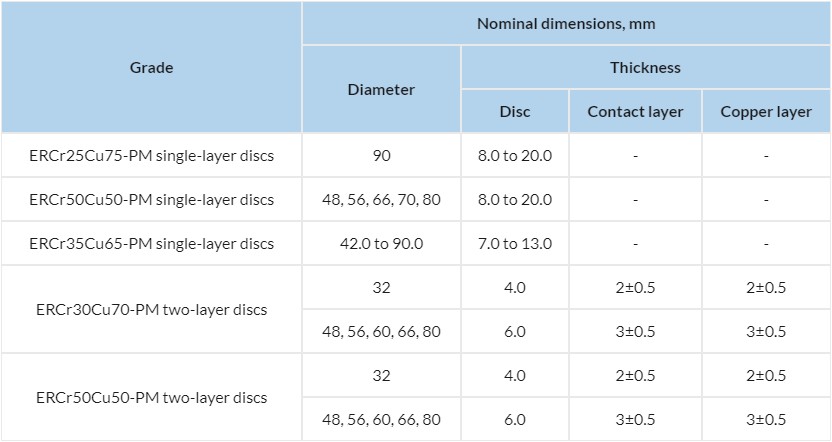
At the client's request, contact parts of other dimensions can be produced.
Physical and mechanical characteristics
| Grade | Minimum density, g/cm³ | Minimum hardness HB* | Minimum conductivity %** |
|---|---|---|---|
| ERCr25Cu75-PM single-layer discs | 8.2 | 65.0 | 55.0 |
| ERCr50Cu50-PM single-layer discs | 7.8 | 90.0 | 40.0 |
| ERCr35Cu65-PM single-layer discs | 8.0 | 72.0 | 45.0 |
| ERCr30Cu70-PM two-layer discs | 8.35 | 70 | 55 |
| ERCr50Cu50-PM two-layer discs | 8.35 | 85 | 40 |
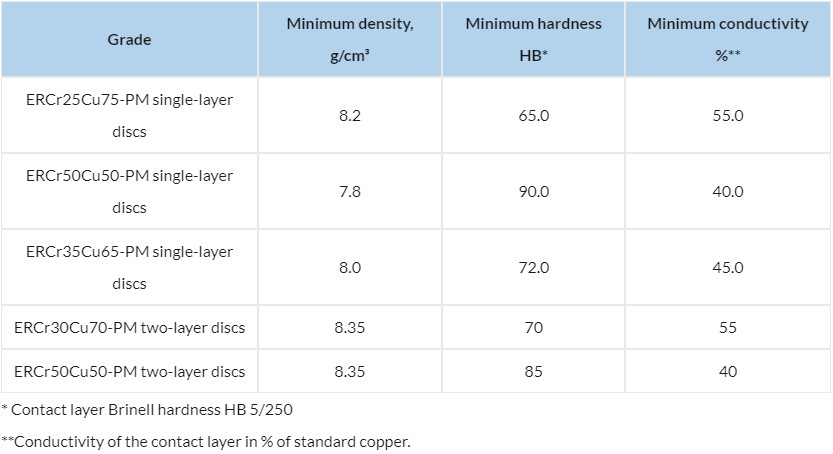
* Contact layer Brinell hardness HB 5/250
**Conductivity of the contact layer in % of standard copper.
Other types of contact parts
Nominal product dimensions, mm: diameter 48, 56, 66, 80 thickness (height) 10. Thickness of contact layer 4.5±0.5 mm.
Contact parts with other dimensions can be produced at the client's request.
Controlled parameters: chemical composition, dimensions, density, hardness and conductivity.
Sample actual specifications of contact parts
| Part | Chemical composition, % | ρ, g/cm³* | HB** | σ, %*** | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | Cu | O max | N max | S max | |||||
| ERCr30Cu70-PM Two-layer disk Ø48x10 | Contact layer | 30.69 | Rem. | 0.025 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 8.59 | 79 | 59.7 |
| Copper substratum | <0.05 | Base | 0.009 | 0.002 | 0.001 | - | - | - | |
| ERCr30Cu70-PM Two-layer disk Ø56x6 | Contact layer | 30.16 | Rem. | 0.026 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 8.54 | 77.1 | 58.7 |
| Copper substratum | <0.05 | Base | 0.01 | 0.002 | 0.001 | - | - | - | |
| ERCr50Cu50-PM Two-layer disk Ø66x6 | Contact layer | 50.3 | Rem. | 0.042 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 8.4 | 106 | 41.1 |
| Copper substratum | <0.05 | Base | 0.008 | 0.002 | 0.001 | - | - | - | |
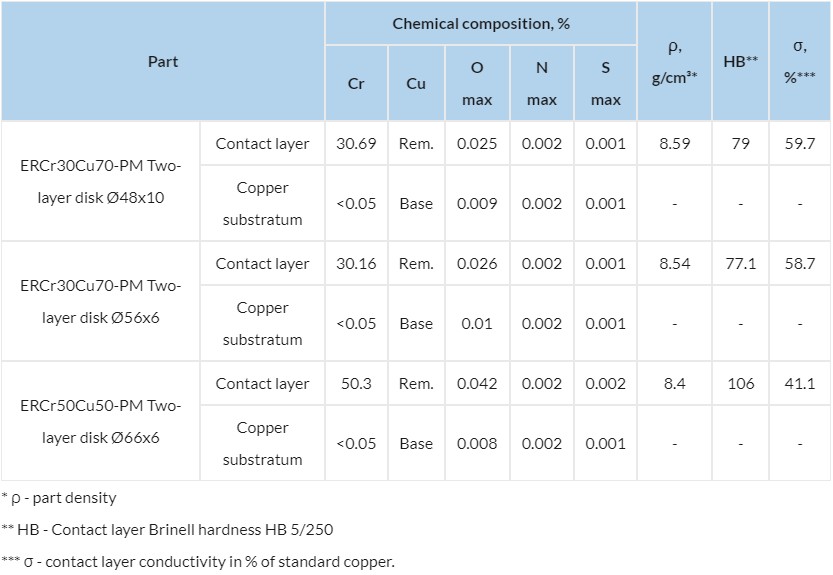
* ρ - part density
** HB - Contact layer Brinell hardness HB 5/250
*** σ - contact layer conductivity in % of standard copper.
Microstructure
In complex parts, material microstructure is monitored to prevent defects and the thicknesses of the contact layer and substratum are checked, along with the quality of the composite's transition layer.
Sample structures of complex contacts
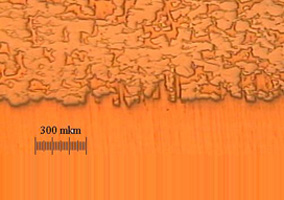
fig. 1
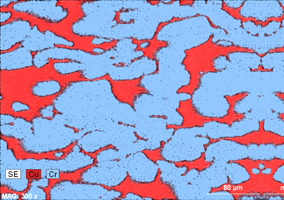
fig. 2
*Fig.1: Complex 2-layer contact material structure ERCr 50Cu50 (fragment). ERCr50Cu50 contact layer and Cu substratum.
*Fig.2: Contact layer structure ERCr30Cu70 (fragment) of bimeitalic contact.
Grade, structure and chemical composition
Contract parts consist of two heterogeneous layers (bimetallic structure): a contact layer made from a tungsten-copper material and a substratum made from copper.
| Grade, standard | Part shape and structure | Chemical composition, mass % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W | Cu | O max | N max | S max | |||
| W70Cu30-PM(elsend) | Bimetallic disks made from W70Cu30 + Cu material | Contact layer | Balance | 28-32 | 0.05 | 0.005 | 0.007 |
| Copper layer | - | Base | 0.02 | 0.005 | 0.007 | ||
PM – Powder Metallurgy
Dimensions
| Grade | Nominal dimensions, mm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter | Thickness | |||
| Disc | Contact layer | Copper layer | ||
| W70Cu30-PM | 32, 48 | 4+2.0 | 2±0.5 | 2±0.5 |
Parts with contacts of other sizes can be produced at the client's request.
Physical and mechanical characteristics

| Grade | Minimum density, g/cm³ | Minimum hardness HB* | Minimum conductivity, %** |
|---|---|---|---|
| W70Cu30-PM | 11.36 | 145 | 55 |
* Contact layer Brinell hardness HB 5/250
** Contact layer conductivity in % of standard copper.
Sample structure of complex contacts
The parts' material microstructure is monitored to prevent defects. The thicknesses of the layers and the quality of the composite's transitional zone are checked.
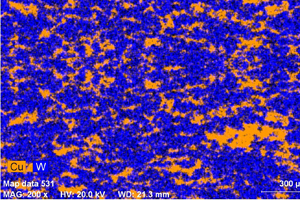
fig. 3
*Fig.3: Structure of bimetal contact layer material W70Cu30-PM (fragment).
Typical specifications:
density 8.86-8.88 g/cm3,
conductivity 87-92%,
hardness 130-140 HB.